
NETGEAR AV Line M4250-10G2XF-PoE+ (GSM4212PX)
8x1G PoE+ 240W 2x1G and 2xSFP+ Managed Switch

Price:
Add to Cart for Pricing
More pricing below, click here!
Overview:
Switching Engineered for AV over IP
Introducing the NETGEAR AV Line of M4250 Switches, developed and engineered for audio/video professionals with dedicated service and support. M4250 has been built from the ground up for the growing AV over IP market, combining years of networking expertise in AV with M4300 and M4500 series with best practices from leading experts in the professional AV market. AV codecs generally use 1Gbps or 10Gbps per stream and the AV Line of M4250 targets the widespread 1Gbps codecs.
PoE+, Ultra90 PoE++ and rear-facing ports ensure a clean integration in AV racks. M4250 switches come pre-configured for standard audio and video signals. When requirements are more specific, an AV user interface offers customization with port-based profiles. For audio Dante, Q-SYS and AES67 profiles are available, as well as an AVB profile requiring an AVB license sold separately. For video the M4250 offers profiles for NVX, AMX, Q-SYS, NDI, Dante etc. as well as audio/ video/control mixed profiles. When multiple switches are used, NETGEAR IGMP PlusTM brings automation for you to just connect them together, or with M4300 and M4500 switches.
Extended AV features
- Dedicated AV web-based GUI interface for more specific AV installations
- Color-based AV profiles can be applied to the different ports
- Dante, Q-SYS, AES67 and AVB audio profiles
- AVB requires a license (sold separately)
- NVX, SVSI, Q-SYS, NDI and Dante video profiles
- Audio / video / control mixed profiles
- Automatic switch interconnect with NETGEAR Auto-Trunk, Auto-LAG and IGMP Plus
- Common Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching engine across all M4250 models
- Built-in IT web GUI, console, telnet and SSH consistent with other NETGEAR M4300 and M4500 series
- Feature set includes static, RIP and PIM routing, DHCP Server and PTPv2
Audio Video Bridging (AVB) services
- AVB is one of the many features designed into the M4250 product line
- AVB is an industry standard for transporting content over a network
- AVB is used most often when very low latency is required such as in live performances when lip sync is critical
- All of the AV Line M4250 switches can be optionally licensed for AVB support
Other IT use cases
- Standard or recessed mounting with all ports in the back, or all ports in the front
- Fully featured L2/L3/L4 platform for midsize Enterprise campus networks, IoT and IPTV
Industry standard management
- Industry standard command line interface (CLI), main NETGEAR IT web interface (GUI), SNMP, sFlow and RSPAN
- Single-pane-of-glass NMS300 management platform with centralized firmware updates and mass-configuration support
Industry leading warranty
- NETGEAR M4250 series is covered under NETGEAR ProSAFE Limited Lifetime Hardware Warranty*
- 90 days of Technical Support via phone and email, Lifetime Technical Support through online chat and Lifetime Next Business Day hardware replacement
Features:
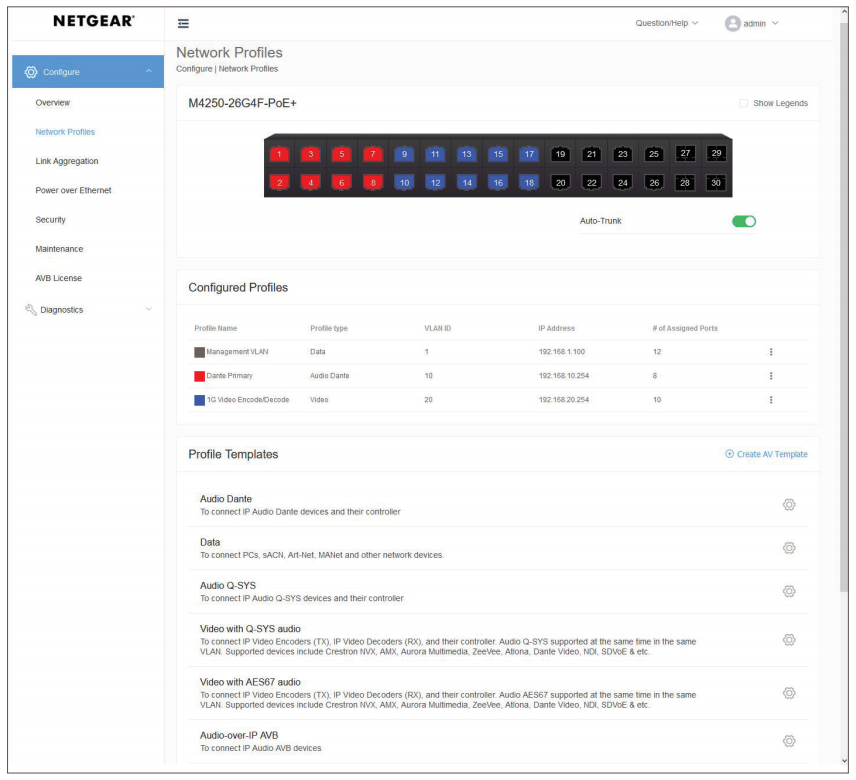
Dedicated AV UI for AV installations
M4250 switch series is pre-configured for Audio and Video over IP out of the box with a dedicated AV web-based GUI interface for more specific AV installations
- Color-based AV profiles can be applied to the different ports
- Dante, Q-SYS, AES67 and AVB audio profiles (AVB license sold separately)
- NVX, AMX, Q-SYS, NDI, Kramer KDS, Aurora Multimedia, ZeeVee, Atlona, Dante, etc. video profiles
- Audio / video / control mixed profiles
Best value switching performance
- 16K MAC address table, 4K ARP and 4K concurrent VLANs for typical midsize environnements
- Low latency at all network speeds, including 10 Gigabit fiber interfaces
- Jumbo frames support of up to 12KB accelerating performance with compatible nodes
- Ranges from 8 to 48 ports with a variety of PoE+ and Ultra90 PoE++ 802.3bt options for 15.4W, 30W, 60W, 75W and 90W AVoIP (1G) endpoints
Tier 1 availability
- Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) and Multiple Spanning Tree (MSTP) allow for rapid transitionning of the ports to the Forwarding state and the suppression of Topology Change Notification
- NETGEAR PVSTP implementation follows the same rules than other vendor’s Per VLAN STP for strict interoperability
- Including industry-standard PVST+ interoperability
- PVSTP is similar to the MSTP protocol as defined by IEEE 802.1s, the main difference being PVSTP runs one instance per VLAN
- In other words, each configured VLAN runs an independent instance of PVSTP
- FastUplink feature immediately moves an alternate port with lowest cost to forwarding state when the root port goes down to reduce recovery time
- FastBackbone feature selects new indirect port when an indirect port fails
- NETGEAR PVRSTP implementation follows the same rules than other vendor’s Per VLAN RSTP for strict interoperability
- Including industry-standard RPVST+ interoperability
- PVRSTP is similar to the RSTP protocol as defined by IEEE 802.1w, the main difference being PVRSTP runs one instance per VLAN
- In other words, each configured VLAN runs an independent instance of PVRSTP
- Each PVRSTP instance elects a root bridge independent of the other
- Hence there are as many Root Bridges in the region as there are VLANs configured
- Per VLAN RSTP has in built support for FastUplink and FastBackbone
- IP address conflict detection performed by embedded DHCP servers prevents accidental IP address duplicates from perturbing the overall network stability
- IP Event Dampening reduces the effect of interface flaps on routing protocols: the routing protocols temporarily disable their processing (on the unstable interface) until the interface becomes stable, thereby greatly increasing the overall stability of the network
Ease of deployment
- Automatic configuration with DHCP and BootP Auto Install eases large deployments with a scalable configuration files management capability, mapping IP addresses and host names and providing individual configuration files to multiple switches as soon as they are initialized on the network
- Both the Switch Serial Number and primary MAC address are reported by a simple "show hardware" command in CLI - facilitating discovery and remote configuration operations
- M4300 DHCP L2 Relay agents eliminate the need to have a DHCP server on each physical network or subnet
- DHCP Relay agents process DHCP messages and generate new DHCP messages
- Supports DHCP Relay Option 82 circuit-id and remote-id for VLANs
- DHCP Relay agents are typically IP routing-aware devices and can be referred to as Layer 3 relay agents
- Automatic Voice over IP prioritization with Auto-VoIP simplifies most complex multi-vendor IP telephones deployments either based on protocols (SIP, H323 and SCCP) or on OUI bytes (default database and user-based OUIs) in the phone source MAC address; providing the best class of service to VoIP streams (both data and signaling) over other ordinary traffic by classifying traffic, and enabling correct egress queue configuration
- An associated Voice VLAN can be easily configured with Auto-VoIP for further traffic isolation
- When deployed IP phones are LLDP-MED compliant, the Voice VLAN will use LLDP-MED to pass on the VLAN ID, 802.1P priority and DSCP values to the IP phones, accelerating convergent deployments
Ease of management and granular control
- Dual firmware image and dual configuration file for transparent firmware updates / configuration changes with minimum service interruption
- Flexible Port-Channel/LAG (802.3ad - 802.1AX) implementation for maximum compatibility, fault tolerance and load sharing with any type of Ethernet channeling from other vendors switch, server or storage devices conforming to IEEE 802.3ad - including static (selectable hashing algorithms) - or to IEEE 802.1AX with dynamic LAGs or port-channel (highly tunable
- LACP Link Aggregation Control Protocol ) LACP mode automatically reverts to and from Static LAG, useful when the host isn’t LACP anymore, for instance during a factory reset or re-configuration
- Auto-LAG: If more than one link between two M4250 switches, a Link Aggregation Group is created, dynamically
- Unidirectional Link Detection Protocol (UDLD) and Aggressive UDLD detect and avoid unidirectional links automatically, in order to prevent forwarding anomalies in a Layer 2 communication channel in which a bi-directional link stops passing traffic in one direction
- Port names feature allows for descriptive names on all interfaces and better clarity in real word admin daily tasks
- SDM (System Data Management, or switch database) templates allow for granular system resources distribution depending on IPv4 or IPv6 applications
- ARP Entries (the maximum number of entries in the IPv4 Address Resolution Protocol ARP cache for routing interfaces)
- IPv4 Unicast Routes (the maximum number of IPv4 unicast forwarding table entries)
- IPv6 NDP Entries (the maximum number of IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol NDP cache entries)
- IPv6 Unicast Routes (the maximum number of IPv6 unicast forwarding table entries)
- ECMP Next Hops (the maximum number of next hops that can be installed in the IPv4 and IPv6 unicast forwarding tables)
- IPv4 Multicast Routes (the maximum number of IPv4 multicast forwarding table entries)
- IPv6 Multicast Routes (the maximum number of IPv6 multicast forwarding table entries)
- Loopback interfaces management for routing protocols administration
- Private VLANs and local Proxy ARP help reduce broadcast with added security
- Management VLAN ID is user selectable for best convenience
- Auto-Trunk: Dynamic VLAN trunking as soon as a M4250 switch gets connected to another M4250 switch
- Industry-standard VLAN management in the command line interface (CLI) for all common operations such as VLAN creation; VLAN names; VLAN “make static” for dynamically created VLAN by GVRP registration; VLAN trunking; VLAN participation as well as VLAN ID (PVID) and VLAN tagging for one interface, a group of interfaces or all interfaces at once
- Simplified VLAN configuration with industry-standard Access Ports for 802.1Q unaware endpoints and Trunk Ports for switch-to-switch links with Native VLAN
- System defaults automatically set per-port broadcast, multicast, and unicast storm control for typical, robust protection against DoS attacks and faulty clients which can, with BYOD, often create network and performance issues
- IP Telephony administration is simplified with consistent Voice VLAN capabilities per the industry standards and automatic functions associated
- Comprehensive set of “system utilities” and “Clear” commands help troubleshoot connectivity issues and restore various configurations to their factory defaults for maximum admin efficiency: traceroute (to discover the routes that packets actually take when traveling on a hop-by-hop basis and with a synchronous response when initiated from the CLI), clear dynamically learned MAC addresses, counters, IGMP snooping table entries from the Multicast forwarding database etc...
- Syslog and Packet Captures can be sent to USB storage for rapid network troubleshooting
- Replaceable factory-default configuration file for predictable network reset in distributed branch offices without IT personnel
- All major centralized software distribution platforms are supported for central software upgrades and configuration files management (HTTP, TFTP), including in highly secured versions (HTTPS, SFTP, SCP)
- Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) can be used to synchronize network resources and for adaptation of NTP, and can provide synchronized network timestamp either in broadcast or unicast mode (SNTP client implemented over UDP - port 123)
- Embedded RMON (4 groups) and sFlow agents permit external network traffic analysis
Engineered for convergence and AV-over-IP
- Audio (Voice over IP) and Video (multicasting) comprehensive switching, filtering, routing and prioritization
- Auto-VoIP, Voice VLAN and LLDP-MED support for IP phones QoS and VLAN configuration
- IEEE 1588 (section 10 and 11.5) PTPv2 Transparent Clock (TC) End-to-End implementation considering the residence time of PTPv2 packets from ingress to egress
- 1-step Transparent Clock mode, using the residence time of the PPTPv2 packet at the egress port level in Standalone mode, or Stack Master only
- The "Sync" & "Delay_Req" fields of passing/egressing out PTPv2 packets are updated with the residence time in the switch, the other fields in PTPv2 packets ("Announce", "Delay_Resp", "Pdelay_Req" and "Pdelay_ Resp") are not updated
- NETGEAR IGMP PlusTM for automatic multicast across a M4250 / M4300 / M4500 L2 network (Spine and Leaf topologies), removing the need for L3 PIM routing
- IGMP Plus is pre-configured on default VLAN 1 out of the box
- IGMP Plus can be configured on another VLAN for automatic IGMP across switches on that VLAN (uplinks can make part of that VLAN in trunk mode) • IGMP Plus allow AV-over-IP devices (TX/Encoders and RX/Decoders) to be connected across multiple switches in a star topology
- The show igmpsnooping group command in CLI and GUI displays the Source and Group IP addresses along with their corresponding MAC addresses that are learnt through IGMP Snooping in a given VLAN on a given interface
- The M4250 series automatically configure the interconnect between switches for robust topologies
- With IGMP Plus, Auto-Trunk and Auto-LAG, your deployment will JUST WORK
- IGMP Snooping and Proxy for IPv4, MLD Snooping and Proxy for IPv6, and Querier mode facilitate fast receivers joins and leaves for multicast streams and ensure multicast traffic only reaches interested receivers everywhere in a Layer 2 or a Layer 3 network, including source-specific (SSM) and any-source (ASM) multicast
- Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR) uses a dedicated Multicast VLAN to forward multicast streams and avoid duplication for clients in different VLANs
- Multicast routing (PIM-SM and PIM-DM, both IPv4 and IPv6) ensure multicast streams can reach receivers in different L3 subnets
- PoE power management and schedule enablement for powering on and powering off PoE nodes connected to the switch
- AVB is one of the many features designed into the M4250 product line
- IEEE 802.1BA-2011 Audio Video Bridging (AVB) when an AVB license is properly installed in the switch (license sold separately)
- IEEE 802.1AS-2011 gPTP, IEEE 802.1Qav-2009 FQTSS, IEEE 802.1Qat-2010 MSRP, IEEE 802.1ak MMRP, IEEE 802.1ak MVRP
- Maximum of 256 AVB streams per switch
- AVB is not supported in LAG (link aggregation groups, or Etherchannel)
Layer 3 routing package
- Static Routes/ECMP Static Routes for IPv4 and IPv6
- Static and default routes are configurable with next IP address hops to any given destination
- Permitting additional routes creates several options for the network administrator
- The admin can configure multiple next hops to a given destination, intending for the router to load share across the next hops
- The admin distinguishes static routes by specifying a route preference value: a lower preference value is a more preferred static route
- A less preferred static route is used if the more preferred static route is unusable (down link, or next hop cannot be resolved to a MAC address)
- Advanced Static Routing functions for administrative traffic control
- Static Reject Routes are configurable to control the traffic destined to a particular network so that it is not forwarded through the router
- Such traffic is discarded and the ICMP destination unreachable message is sent back to the source
- Static reject routes can be typically used to prevent routing loops
- Default routes are configurable as a preference option
- In order to facilitate VLAN creation and VLAN routing using Web GUI, a VLAN Routing Wizard offers following automated capabilities:
- Create a VLAN and generate a unique name for VLAN
- Add selected ports to the newly created VLAN and remove selected ports from the default VLAN
- Create a LAG, add selected ports to a LAG, then add this LAG to the newly created VLAN
- Enable tagging on selected ports if the port is in another VLAN
- Disable tagging if a selected port does not exist in another VLAN
- Exclude ports that are not selected from the VLAN
- Enable routing on the VLAN using the IP address and subnet mask entered as logical routing interface
- DHCP Relay Agents relay DHCP requests from any routed interface, including VLANs, when DHCP server doesn’t reside on the same IP network or subnet
- The agent relays requests from a subnet without a DHCP server to a server or next-hop agent on another subnet
- Unlike a router which switches IP packets transparently, a DHCP relay agent processes DHCP messages and generates new DHCP messages
- Supports DHCP Relay Option 82 circuit-id and remote-id for VLANs
- Multiple Helper IPs feature allows to configure a DHCP relay agent with multiple DHCP server addresses per routing interface and to use different server addresses for client packets arriving on different interfaces on the relay agent server addresses for client packets arriving on different interfaces on the relay agent
- Router Discovery Protocol is an extension to ICMP and enables hosts to dynamically discover the IP address of routers on local IP subnets
- Based on RFC 1256 for IPv4
- Routers periodically send router discovery messages to announce their presence to locally-attached hosts
- The router discovery message advertises one or more IP addresses on the router that hosts can use as their default gateway
- Hosts can send a router solicitation message asking any router that receives the message to immediately send a router advertisement
- Router discovery eliminates the need to manually configure a default gateway on each host
- It enables hosts to switch to a different default gateway if one goes down
- Loopback interfaces are available as dynamic, stable IP addresses for other devices on the network, and for routing protocols
- Support of Routing Information Protocol (RIPv2) as a distance vector protocol specified in RFC 2453 for IPv4
- Each route is characterized by the number of gateways, or hops, a packet must traverse to reach its intended destination
- Categorized as an interior gateway protocol, RIP operates within the scope of an autonomous system
- IP Multinetting allows to configure more than one IP address on a network interface (other vendors may call it IP Aliasing or Secondary Addressing)
- ICMP Throttling feature adds configuration options for the transmission of various types of ICMP messages
- ICMP Redirects can be used by a malicious sender to perform man-in-the-middle attacks, or divert packets to a malicious monitor, or to cause Denial of Service (DoS) by blackholing the packets • ICMP Echo Requests and other messages can be used to probe for vulnerable hosts or routers
- Rate limiting ICMP error messages protects the local router and the network from sending a large number of messages that take CPU and bandwidth
- The Policy Based Routing feature (PBR) overrides routing decision taken by the router and makes the packet to follow different actions based on a policy
- It provides freedom over packet routing/forwarding instead of leaving the control to standard routing protocols based on L3
- For instance, some organizations would like to dictate paths instead of following the paths shown by routing protocols
- Network Managers/Administrators can set up policies such as:
– My network will not carry traffic from the Engineering department
– Traffic originating within my network with the following characteristics will take path A, while other traffic will take path B
– When load sharing needs to be done for the incoming traffic across multiple paths based on packet entities in the incoming traffic
Enterprise security
- Traffic control MAC Filter and Port Security help restrict the traffic allowed into and out of specified ports or interfaces in the system in order to increase overall security and block MAC address flooding issues
- DHCP Snooping monitors DHCP traffic between DHCP clients and DHCP servers to filter harmful DHCP message and builds a bindings database of (MAC address, IP address, VLAN ID, port) tuples that are considered authorized in order to prevent DHCP server spoofing attacks
- IP source guard and Dynamic ARP Inspection use the DHCP snooping bindings database per port and per VLAN to drop incoming packets that do not match any binding and to enforce source IP/MAC addresses for malicious users traffic elimination
- Time-based Layer 2 / Layer 3-v4 / Layer 3-v6 / Layer 4 Access Control Lists (ACLs) can be binded to ports, Layer 2 interfaces, VLANs and LAGs (Link Aggregation Groups or Port channel) for fast unauthorized data prevention and right granularity
- For in-band switch management, management ACLs on CPU interface (Control Plane ACLs) are used to define the IP/MAC or protocol through which management access is allowed for increased HTTP/HTTPS or Telnet/SSH management security
- Out-of-band management is available via dedicated service port (1G RJ45 OOB) when in-band management can be prohibited via management ACLs
- Bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) Guard allows the network administrator to enforce the Spanning Tree (STP) domain borders and keep the active topology consistent and predictable - unauthorized devices or switches behind the edge ports that have BPDU enabled will not be able to influence the overall STP by creating loops
- Spanning Tree Root Guard (STRG) enforces the Layer 2 network topology by preventing rogue root bridges potential issues when for instance, unauthorized or unexpected new equipment in the network may accidentally become a root bridge for a given VLAN
- Dynamic 802.1x VLAN assignment mode, including Dynamic VLAN creation mode and Guest VLAN / Unauthenticated VLAN are supported for rigorous user and equipment RADIUS policy server enforcement
- Up to 48 clients (802.1x) per port are supported, including the authentication of the users domain, in order to facilitate convergent deployments. For instance when IP phones connect PCs on their bridge, IP phones and PCs can authenticate on the same switch port but under different VLAN assignment policies (Voice VLAN versus other Production VLANs)
- 802.1x MAC Address Authentication Bypass (MAB) is a supplemental authentication mechanism that lets non-802.1x devices bypass the traditional 802.1x process altogether, letting them authenticate to the network using their client MAC address as an identifier
- A list of authorized MAC addresses of client NICs is maintained on the RADIUS server for MAB purpose
- MAB can be configured on a per-port basis on the switch
- MAB initiates after unsuccessful dot1x authentication process (configurable time out), when clients don’t respond to any of EAPOL packets
- When 802.1X unaware clients try to connect, the switch sends the MAC address of each client to the authentication server
- The RADIUS server checks the MAC address of the client NIC against the list of authorized addresses
- The RADIUS server returns the access policy and VLAN assignment to the switch for each client
- With Successive Tiering, the Authentication Manager allows for authentication methods per port for a Tiered Authentication based on configured time-outs
- By default, configuration authentication methods are tried in this order: Dot1x, then MAB, then Captive Portal (web authentication)
- With BYOD, such Tiered Authentication is powerful and simple to implement with strict policies – For instance, when a client is connecting, M4300 tries to authenticate the user/client using the three methods above, the one after the other
- The admin can restrict the configuration such that no other method is allowed to follow the captive portal method, for instance
- Double VLANs (DVLAN) pass traffic from one customer domain to another through the “metro core” in a multi-tenancy environment: customer VLAN IDs are preserved and a service provider VLAN ID is added to the traffic so the traffic can pass the metro core in a simple, secure manner
- Private VLANs (with Primary VLAN, Isolated VLAN, Community VLAN, Promiscuous port, Host port, Trunks) provide Layer 2 isolation between ports that share the same broadcast domain, allowing a VLAN broadcast domain to be partitioned into smaller point-to-multipoint subdomains accross switches in the same Layer 2 network
- Private VLANs are useful in DMZ when servers are not supposed to communicate with each other but need to communicate with a router
- They remove the need for more complex port-based VLANs with respective IP interface/subnets and associated L3 routing
- Another Private VLANs typical application are carrier-class deployments when users shouldn’t see, snoop or attack other users’ traffic
- SSL version 3 and TLS version 2 ensure Web GUI sessions are secured
- Secure Shell (SSH version 2) and SNMPv3 (with or without MD5 or SHA authentication) ensure SNMP and Telnet sessions are secured
- 2048-bit RSA key pairs, SHA2-256 and SHA2-512 cryptographic hash functions for SSLv3 and SSHv2 are supported on all M4300 models
- TACACS+ and RADIUS enhanced administrator management provides strict “Login” and “Enable” authentication enforcement for the switch configuration, based on latest industry standards: exec authorization using TACACS+ or RADIUS; command authorization using TACACS+ and RADIUS Server; user exec accounting for HTTP and HTTPS using TACACS+ or RADIUS; and authentication based on user domain in addition to user ID and password
Superior quality of service
- Advanced classifier-based hardware implementation for Layer 2 (MAC), Layer 3 (IP) and Layer 4 (UDP/TCP transport ports) prioritization
- 8 queues (7 in a stack) for priorities and various QoS policies based on 802.1p (CoS) and DiffServ can be applied to interfaces and VLANs
- Advanced rate limiting down to 1 Kbps granularity and mininum-guaranteed bandwidth can be associated with ACLs for best granularity
- Single Rate Policing feature enables support for Single Rate Policer as defined by RFC 2697
- Committed Information Rate (average allowable rate for the class)
- Committed Burst Size (maximum amount of contiguous packets for the class)
- Excessive Burst Size (additional burst size for the class with credits refill at a slower rate than committed burst size)
- DiffServ feature applied to class maps
- Automatic Voice over IP prioritization with protocol-based (SIP, H323 and SCCP ) or OUI-based Auto-VoIP up to 144 simultaneous voice calls
Flow Control
- 802.3x Flow Control implementation per IEEE 802.3 Annex 31B specifications with Symmetric flow control, Asymmetric flow control or No flow control
- Asymmetric flow control allows the switch to respond to received PAUSE frames, but the ports cannot generate PAUSE frames
- Symmetric flow control allows the switch to both respond to, and generate MAC control PAUSE frames
- Allows traffic from one device to be throttled for a specified period of time: a device that wishes to inhibit transmission of data frames from another device on the LAN transmits a PAUSE frame
- A device that wishes to inhibit transmission of data frames from another device on the LAN transmits a PAUSE frame
UDLD Support
- UDLD implementation detects unidirectional links physical ports (UDLD must be enabled on both sides of the link in order to detect an unidirectional link)
- UDLD protocol operates by exchanging packets containing information about neighboring devices
- The purpose is to detect and avoid unidirectional link forwarding anomalies in a Layer 2 communication channel
- Both “normal-mode” and “aggressive-mode” are supported for perfect compatibility with other vendors implementations, including port “D-Disable” triggering cases in both modes
At a Glance:
| Hardware at a glance | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rear | LEDS | Management | |||||||
| Model name | Form-Factor | Switching Fabric | 10/100/1000BASE-TRJ45 ports | 100/1000/2.5GBASE-T RJ45 ports | 1000BASE-X SFP ports | 1000/10GBASE-X SFP+ ports | PSU | Status Information | Out-of-band Console |
| M4250-9G1F-PoE+ (GSM4210PD) | Desktop 210 x 40 x 140mm |
20 Gbps | 8 ports PoE+ (110W) 1 additional port | - | 2 ports SFP 1G | - | 1 x External Power Adapter (130W) | In Front: Power LED PoE Max LED Fan LED (GSM4210PX only) |
Ethernet: 1G Out-of-band (Rear) Console: USB-C (Front) Storage: USB-A (Rear) |
| M4250-8G2XF-PoE+ (GSM4210PX) | Desktop 210 x 40 x 140mm |
56 Gbps | 8 ports PoE+ (220W) | - | - | 2 ports SFP+ 1G; 10G | 1 x External Power Adapter (254W) | ||
| M4250-10G2F-PoE+ (GSM4212P) | 1U rackmount 440 x 43.2 x 200mm |
24 Gbps | 8 ports PoE+ (125W) 2 additional ports | - | 2 ports SFP 1G | - | 1 x Fixed (C14) On/off switch | Available both in front and in the rear: Power LED PoE Max LED (PoE models) Fan LED Port LEDs |
Ethernet: 1G Out-of-band (Rear) Console: RJ45 RS232 (Rear) Console: USB-C (Rear) Storage: USB-A (Front) LED Ext: USB-C (Front) |
| M4250-10G2XF-PoE+ (GSM4212PX) | 1U rackmount 440 x 43.2 x 200mm |
60 Gbps | 8 ports PoE+ (125W) 2 additional ports | - | - | 2 ports SFP+ 1G, 10G | 1 x Fixed (C14) On/off switch | ||
| M4250-10G2XF-PoE++ (GSM4212UX) | 1U rackmount 440 x 43.2 x 257mm |
60 Gbps | 8 ports PoE++** (720W) 2 additional ports | - | - | 2 ports SFP+ 1G, 10G | 1 x Fixed (C14) On/off switch | ||
| M4250-12M2XF (MSM4214X) | 1U rackmount 440 x 43.2 x 300mm |
100 Gbps | - | 12 ports 100M, 1G, 2.5G | - | 2 ports SFP+ 1G, 10G | 1 x Fixed (C14) On/Off switch | ||
| M4250-16XF (XSM4216F) | 1U rackmount 440 x 43.2 x 200mm |
320 Gbps | - | - | - | 16 ports SFP+ 1G, 10G | 1 x Fixed (C14) On/Off switch | ||
| M4250-26G4F-PoE+ (GSM4230P) | 1U rackmount 440x43.2x257mm | 60 Gbps | 24 ports PoE+ (300W) 2 additional ports | - | 4 ports SFP 1G | - | 1 x Fixed (C14) On/Off switch | ||
| M4250-26G4F-PoE++ (GSM4230UP) | 1U rackmount 440x43.2x400mm | 60 Gbps | 24 ports PoE++ (1,440W)** (1 PSU/720W; 2 PSU/1,440W) 2 additional ports |
- | 4 ports SFP 1G | - | 2 x Fixed (C14) On/Off switch | ||
| M4250-26G4XF-PoE+ (GSM4230PX) | 1U rackmount 440x43.2x400mm | 132 Gbps | 24 ports PoE+ (480W) 2 additional ports | - | - | 4 ports SFP+ 1G; 10G | 1 x Fixed (C14) On/Off switch | ||
| M4250-40G8F-PoE+ (GSM4248P) | 1U rackmount 440x43.2x400mm |
96 Gbps | 40 ports PoE+ (480W) | - | 8 ports SFP 1G | - | 1 x Fixed (C14) On/Off switch | ||
| M4250-40G8XF-PoE+ (GSM4248PX) | 1U rackmount 440x43.2x400mm |
240 Gbps | 40 ports PoE+ (960W) | - | - | 8 ports SFP+ 1G; 10G | 1 x Fixed (C14) On/Off switch | ||
| M4250-40G8XF-PoE++ (GSM4248UX) | 2U rackmount 440x86.4x350mm |
240 Gbps | 40 ports PoE++ (2,880W)** (1 PSU/720W; 2 PSU/1,650W; 3 PSU/2,880W) |
- | - | 8 ports SFP+ 1G; 10G | 3 x Fixed (C14) On/Off switch | ||
| Software at a glance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer 3 Package | ||||||
| Model name | Management | AV Dedicated UI | IPv4 / IPv6 ACL and QoS, DiffServ |
IPv4 / IPv6 Multicast Filtering | IPv4 / IPv6 Policing and Convergence |
Spanning Tree Green Ethernet |
| M4250 Series | Out-of-band IT Web GUI (main) HTTPs CLI; Telnet; SSH SNMP, MIBs RSPAN Radius Users, TACACS+ |
AV web-based GUI Designed for AV installers AV-related controls Audio over IP profiles AVB profile* Video over IP profiles Mixed Audio and Video profiles |
Ingress/egress 1 Kbps shaping Time-based Single Rate Policing |
NETGEAR IGMPTM Plus for automated IGMP between switches IGMPv3 MLDv2 Snooping, Proxy ASM & SSM IGMPv1,v2 Querier (compatible v3) Control Packet Flooding |
Auto-VoIP Policy-based routing (PBR) LLDP-MED IEEE 1588 PTPv2 1-Step End-to-End Transparent Clock AVB*: 802.1AS, 802.1Qav, 802.1Qat MSRP, 802.1ak MMRP, 802.1ak MVRP |
STP, MTP, RSTP PV(R)STP BPDU/STRG Root Guard EEE 802.3az (EEE is disabled by default) |
| Layer 3 Package | ||||||
| Model name | VLANs | Trunking Port Channel | IPv4 / IPv6 Authentication Security | IPv4 / IPv6 Static Routing | IPv4 / IPv6 Dynamic Routing | |
| M4250 Series | Static, Dynamic, Voice, MAC GVRP/GMRP Double VLAN mode Private VLANs |
Auto-Trunk and Auto-LAG between M4250 Switches Static LAG, or Dynamic LACP (LACP automatically reverts to and from Static LAG) Seven (7) L2/L3/L4 hashing algorithms |
Successive Tiering (DOT1X; MAB; Captive Portal) DHCP Snooping Dynamic ARP Inspection IP Source Guard |
Port, Subnet, VLAN routing Multicast static routes DHCPv4 Server DHCP Relay Stateful DHCPv6 Server |
IPv4: RIP IPv4/IPv6: PIM-SM PIM-DM SSM |
|
| Performance at a Glance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table Size | ||||||
| Model name | MAC ARP/ NDP | Routing / Switching Capacity | Throughput | Application Route Scaling | Packet Buffer | Latency |
| M4250-9G1F-PoE+ (GSM4210PD) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 20 Gbps Line-Rate | 14.88 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <2.27µs 1G |
| M4250-8G2XF-PoE+ (GSM4210PX) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 56 Gbps Line-Rate | 41.67 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <2.14µs 1G <0.84µs 10G |
| M4250-10G2F-PoE+ (GSM4212P) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 24 Gbps Line-Rate | 17.86 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <2.27µs 1G |
| M4250-10G2XF-PoE+ (GSM4212PX) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 60 Gbps Line-Rate | 44.64 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <2.14µs 1G <0.84µs 10G |
| M4250-10G2XF-PoE++ (GSM4212UX) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 60 Gbps Line-Rate | 44.64 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <1.84µs 1G <0.81µs 10G |
| M4250-12M2XF (MSM4214X) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 100 Gbps Line-Rate | 74.40 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <2.84.µs 1G <6.02µs 2.5G <0.81µs 10G |
| M4250-16XF (XSM4216F) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 320 Gbps Line-Rate | 238.08 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <1.30µs 1G <0.86µs 10G |
| M4250-26G4F-PoE+ (GSM4230P) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 60 Gbps Line-Rate | 44.64 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <2.15.µs 1G |
| M4250-26G4F-PoE++ (GSM4230UP) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/NDP | 60 Gbps Line-Rate | 44.64 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <2.15.µs 1G |
| M4250-26G4XF-PoE+ (GSM4230PX) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 60 Gbps Line-Rate | 98.21 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
16Mb | <2.29µs 1G <0.83µs 10G |
| M4250-40G8F-PoE+ (GSM4248P) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 96 Gbps Line-Rate | 71.42 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
32Mb | <2.46µs 1G |
| M4250-40G8XF-PoE+ (GSM4248PX) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 240 Gbps Line-Rate | 178.56 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
32Mb | <2.74µs 1G <0.73µs 10G |
| M4250-40G8XF-PoE++ (GSM4248UX) | 16K MAC 4K ARP/ NDP | 240 Gbps Line-Rate | 178.56 Mpps | Static: 894v4/126v6 RIP: 32v4 |
32Mb | <2.78µs 1G <0.73µs 10G |
| Table Size | ||||||
| Model name | CPU | IP Multicast Routing Entries |
Jumbo Frames | Multicast IGMP Group membership |
VLANs | DHCP |
| M4250-9G1F-PoE+ (GSM4210PD) | ARM A9 1.25Ghz 32-Bit 2GB RAM |
512 IPv4 128 IPv6 | Up to 12K | 2K IPv4 2K IPv6 |
4K VLANs | DHCP Server: 2K leases IPv4: 256 pools IPv6: 16 pools |
| M4250-8G2XF-PoE+ (GSM4210PX) | ||||||
| M4250-10G2F-PoE+ (GSM4212P) | ||||||
| M4250-10G2XF-PoE+ (GSM4212PX) | ||||||
| M4250-10G2XF-PoE++ (GSM4212UX) | ||||||
| M4250-12M2XF (MSM4214X) | ||||||
| M4250-16XF (XSM4216F) | ||||||
| M4250-26G4F-PoE+ (GSM4230P) | Quad-Core Cortex-A57 ARMv8 1.8Ghz 64-bit 2GB RAM |
|||||
| M4250-26G4F-PoE++ (GSM4230UP) | ||||||
| M4250-26G4XF-PoE+ (GSM4230PX) | ||||||
| M4250-40G8F-PoE+ (GSM4248P) | ||||||
| M4250-40G8XF-PoE+ (GSM4248PX) | ||||||
| M4250-40G8XF-PoE++ (GSM4248UX) | ||||||
Specifications:

M4250-10G2XF-PoE+ Front

M4250-10G2XF-PoE+ Back
| Models: | M4250-10G2XF-PoE+ (GSM4212PX) |
|---|---|
| General |
|
| Key Features |
|
| AV Software Features |
|
| Other Software Features |
|
| Management Features |
|
| Warranty and Support |
|
Network Diagram:
Target Application
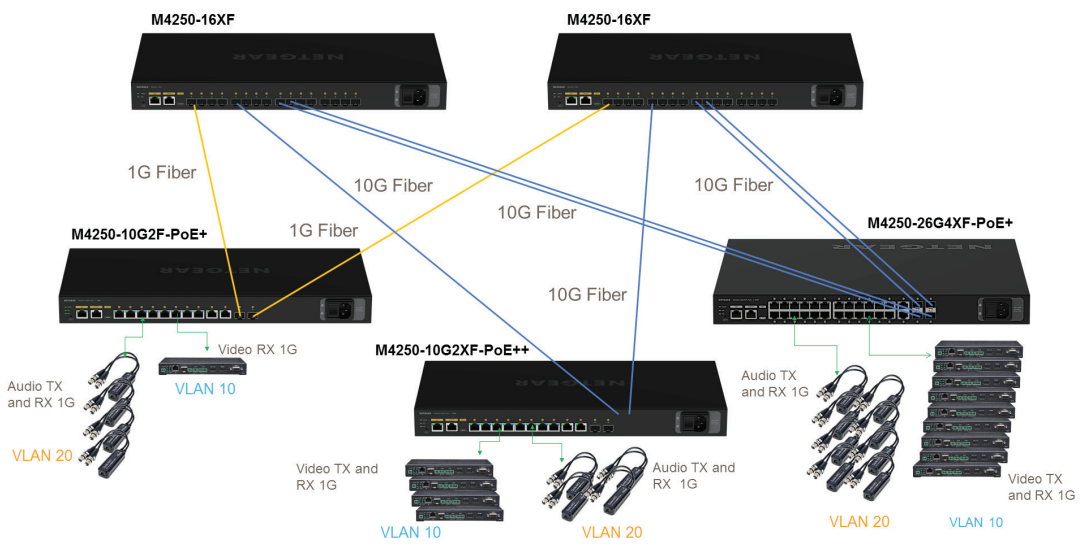
A new AV Line of M4250 switches with out-of-the-box functionality and an industry-first: a concurrent second user interface solely designed with the AV Pro in mind.
NETGEAR has enhanced the experience for AV professionals by including a new user interface designed from the ground up. Pro AV customers don’t have to settle for an IT-centric interface with settings and IT-specific functionality they will never need. The new M4250 AV interface presents the common AV controls right up front with user-selectable profiles for common AV platforms making it a snap to ensure the settings are correct for a specific audio or video application.
When each M4250 is simply configured with AV profiles on certain ports, the AV Line offers automatic and dynamic configuration of multiple M4250 switches connected together. This automatic configuration, known as Auto-LAG and Auto-Trunk, combined with as NETGEAR IGMP Plus™, make setting up a complicated AV over IP network easier and quicker than ever before.
Documentation:
Download the NETGEAR M4250 Series AV Line Managed Switches Datasheet (PDF).
Pricing Notes:
- Pricing and product availability subject to change without notice.
Price:
Add to Cart for Pricing

